EMS providers should have a good understanding of epidural and subdural hematomas, as prompt recognition and management are crucial.
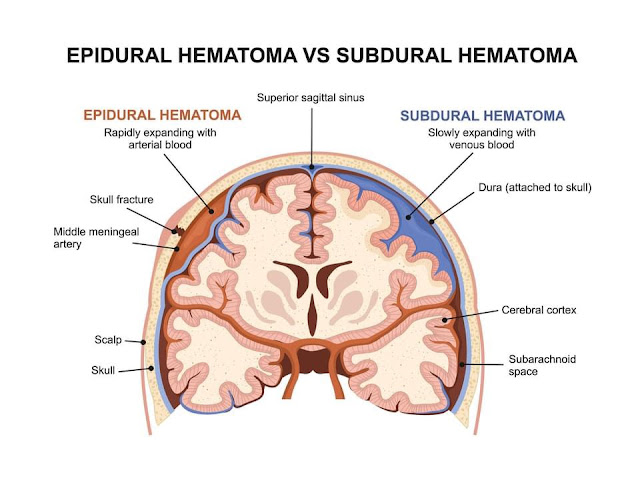
An epidural hematoma occurs when blood accumulates between the skull and the outer layer of the brain (dura mater). It is typically caused by a traumatic head injury, such as a skull fracture that damages the middle meningeal artery.
Examples of causes include motor vehicle accidents, falls, or assaults.
A subdural hematoma, on the other hand, is the accumulation of blood between the dura mater and the brain. It can result from a direct blow to the head or rotational forces causing tearing of the bridging veins.
Causes can include falls, sports injuries, shaken baby syndrome, or head trauma in older adults due to minor falls.
In both cases, the accumulation of blood can lead to increased pressure on the brain, potentially causing neurological deficits.
EMS Providers should be aware of the signs and symptoms, such as severe headache, altered mental status, focal neurological deficits, or changes in consciousness.
Prompt transportation to a trauma center is essential for definitive diagnosis and surgical intervention, if necessary.
Remember, this information is not a substitute for medical advice. If you suspect a head injury, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
#PreHospitalCare #TraumaEmergencies #EpiduralHematoma #SubduralHematoma #NeurologicalDeficits
No comments:
Post a Comment